State Handling in React JS
React's component-based architecture enables developers to create reusable, composable UI elements. However, as applications grow in complexity, managing the state of these components becomes crucial for maintaining a predictable and efficient user experience.
In React, state refers to the data that determines a component's behavior and rendering. It encapsulates the current state of a component and influences its appearance and interactions. Understanding how to manage state effectively is fundamental to building robust and scalable React applications.
In this article, we'll dive into the fundamentals of state handling in React, exploring various techniques and best practices for managing state within components. We'll cover local component state, and application level state handling techniques with libraries like Redux, Zustand, and Context API. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of which path to choose for difference scenarios.
State Management Flow Chart
#| Method | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|
| useState (component) | Scoped to a single component | selected state in Single Component (product-variations/index.jsx) The property is used only in this component. |
| useState (page) | Scoped to a single page | isOverlayOpen state in CustomizationContainer (customization-component.js) The property is part of an object that is passed as a prop to AddToCartModalComponent (and no further). |
| Context API | Prop drill is needed for more than one level | PDP, where we might have component/page state for "selected option set" and some deep component needs to know about it. |
| Zustand/Redux | Needed across the application and is based on user action, whether that be: - Direct input (Eg. deliveryInfo.phone) - Selection of explicit options (Eg. fulfillmentDate) - Selection of implicit options (Eg. storeId) - System assigned value that can’t be querieddirectly (Eg. orderId) | In addition to the use case-specific examples at left, you can find the rest of the global store in /stores |
| SWR Hook | - Managing data fetching and server managed state - useSWR is able to fetch backend data, as well as manage caching for redundant requests - Supports traditional HTTP requests as well as graphQL queries. | |
| URL query params | When page level state needs to be set from outside of the page. | Passing an orderId from an email, etc. |
Application Flow
#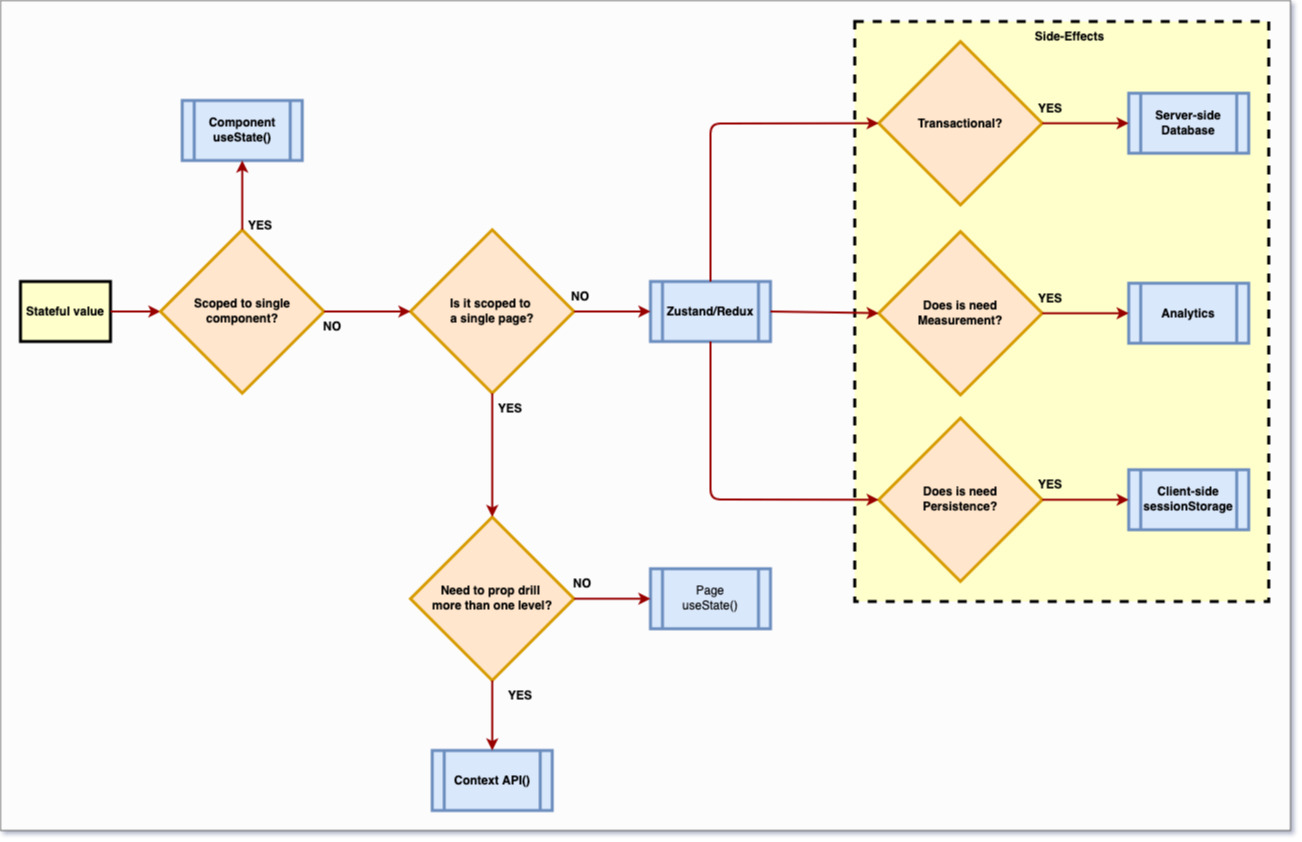
With the help of above example, you can decide which path to got with.